

Product with time reduced price

Wild currant seeds (Grewia...
- -€0.01








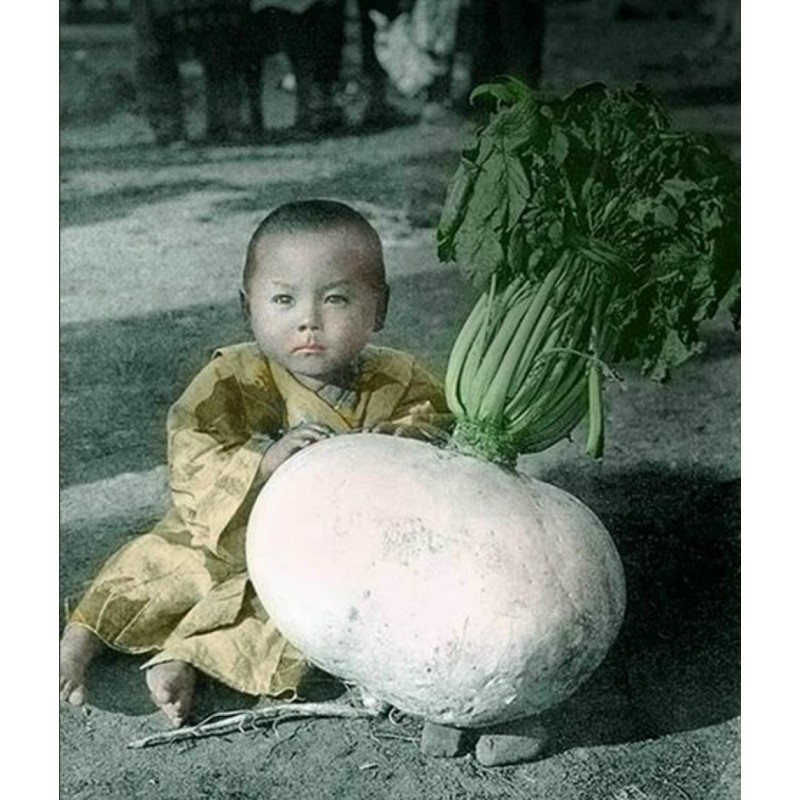
The Sakurajima Radish is known as the “Largest Radish in the World.” It has produced radishes at a standard weight of 13 pounds and is capable of reaching 100 pounds! This traditional variety of daikon radish has a
The Sakurajima Radish is known as the “Largest Radish in the World.” It has produced radishes at a standard weight of 13 pounds and is capable of reaching 100 pounds! This traditional variety of daikon radish has a round basketball-like shape, unlike its longer and skinnier daikon relatives. Daikon radishes were introduced to Japan over 1,300 years ago, and there are over 120 varieties with unique characteristics cultivated regionally. During the Edo Period (1603-1868), daikons became extremely popular, and today 90% of daikons are produced and consumed in Japan. However, the regional varieties have slowly been replaced by the F1 hybrid variety called Aokubi. Aokubi and other F1 hybrids now account for the majority of the daikon production.
The Sakurajima Radish represents one of the few regionally cultivated varieties of daikon still being grown in Japan. Named after its place of cultivation, the former island of Sakurajima in Japan's Kagoshima Prefecture, the radish is thought to have been grown since at least 1804 and most likely before this date. Sakurajima was the southernmost island in the Kagoshima Prefecture with volcanic soils where rice would not thrive. In place of rice, the mammoth white radish was grown in mass amounts as a commercial crop and hauled to Kagoshima City to trade for straw. At the height of its production, as much as 500 acres would be planted each year.
Although the region has a long history of volcanic activity that began to impact the production of this magnificent radish. Sakurajima is a composite of mountains with three peaks that express volcanic activity. The first recorded volcanic eruption occurred in 963 A.D. Smaller eruptions occur constantly. Sometimes 1,000 eruptions can occur in a year, although larger eruptions have been recorded in the 1400s, 1700s and more recently in 1914.
The 1914 eruption instigated lava flows that lasted for months. The lava connected Sakurajima Island to the Osumi Penninsula by a thin isthmus, attaching it to the mainland and taking away its island status. The enormity of the 1914 eruption significantly decreased the land available to grow the staple crop. Since 1955, ash has been dropping consistently and has created challenging growing conditions. As a result, the growing area was decreased to as little as 3.5 acres by 2001. In August of 2015, the Japanese Meteorological Agency gave the volcano a Level 3 (Orange Alert), warning people that the volcano is active and should not be approached.
As a traditional crop, it continues to have a key role in Japanese cuisine. Sakurajima Radish can be pickled in a salt brine and used as a tsukemono, or “pickled things.” The large radish is known for having a sweeter and firmer flesh than other daikon varieties. It also stores well in potato-like storage conditions. Therefore, it is well suited for simmering and for being used in soups, as it will keep its structure and firm texture. While the Sakurajima Radish is no longer a key commercial crop of the region, it remains a beloved traditional crop. Recently the growing area has begun to expand again for its production.
Data sheet
Radishes are a hardy, easy-to-grow root vegetable that can be planted multiple times in a growing season.
Here’s how to plant and grow radishes in your garden!
Radish seeds can be planted in both the spring and the fall, but growth should be suspended in the height of summer when temperatures are typically too hot. (Hot temperatures may cause radishes to bolt, making them essentially useless.)
Otherwise, radishes are one of the easiest vegetables to grow.
Plant in a sunny spot. If radishes are planted in too much shade—or even where neighboring vegetable plants shade them—they will put all their energy into producing larger leaves.
Like carrots, radish plants are primarily grown for their roots. Though the soil needs to be rich in organic matter, it should not be compacted. If your soil is more clay-like, mix in some sand to loosen it and improve drainage.
If your soil isn’t rich in organic matter, incorporate a few inches of aged compost or all-purpose fertilizer (see packaging for amount) into the planting site as soon as the soil is workable.
Till your garden bed to remove any rocks or dirt clods before planting.
Practice three-year crop rotation. In other words, only plant radishes in the same spot every third year. This will help prevent diseases from affecting your crop.
For a spring planting, sow seeds 4–6 weeks before the average date of the last frost. See local frost dates here.
It’s best to plant radish seeds directly in the garden so as not to disturb their roots. Directly sow seeds outdoors 2 cm deep and 2,5 cm apart in rows 28 cm apart.
Plant another round of seeds every 10 days or so—while weather is still cool—for a continuous harvest of radishes in the late spring and early summer.
Plan on a fall planting. You can plant radishes later than any other root crop in late summer or early fall and still get a harvest. Sow seeds 4–6 weeks before the first fall frost.
Thin radishes to about 2 inches apart when the plants are a week old. Crowded plants do not grow well.
Consistent, even moisture is key. Keep soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. A drip irrigation system is a great way to achieve this.
Putting a thin layer of mulch around the radishes can help retain moisture in dry conditions.
Radishes will be ready to harvest quite rapidly, as soon as three weeks after planting for some varieties.
For most varieties, harvest when roots are approximately 2,5 cm in diameter at the soil surface. Pull one out and test it before harvesting the rest!
Do not leave radishes in the ground long after their mature stage; their condition will deteriorate quickly.
Cut the tops and the thin root tail off, wash the radishes, and dry them thoroughly. Store in plastic bags in the refrigerator.
Radish greens can be stored separately for up to three days.
Radish seeds have a fairly long shelf life. Don’t be afraid to plant radish seeds that are up to five years old. All may not germinate, but you’ll have plenty that will.
 Reviews (0)
Reviews (0)